Unlock the Power of Skill Progressions
February 2, 2026
Teachers should use skill progressions in reading and writing every day. They clarify how skills build over time and in across increasingly complex texts and tasks, providing a roadmap to support students as they move forward with their learning. They make it easy for teachers to match assessment data to targeted strategies, and align strategy instruction with grade-level standards. Teaching students the right strategy at the right time advances and accelerates their learning.
Leveraging Skill Progressions: Reading Instruction
Begin with the text: look closely at what it demands of readers, noting which complexities or features might present new challenges for your students. Revisit your lesson objective and the specific skills students need to work on and the standards they address. Within each reading skill progression, students develop multiple proficiencies that grow in sophistication as they encounter increasingly complex texts. Use the progression as a guide to pinpoint where each student is in their learning and to select a strategy that aligns with both the demands of the text and the phase of skill development the student is currently navigating.
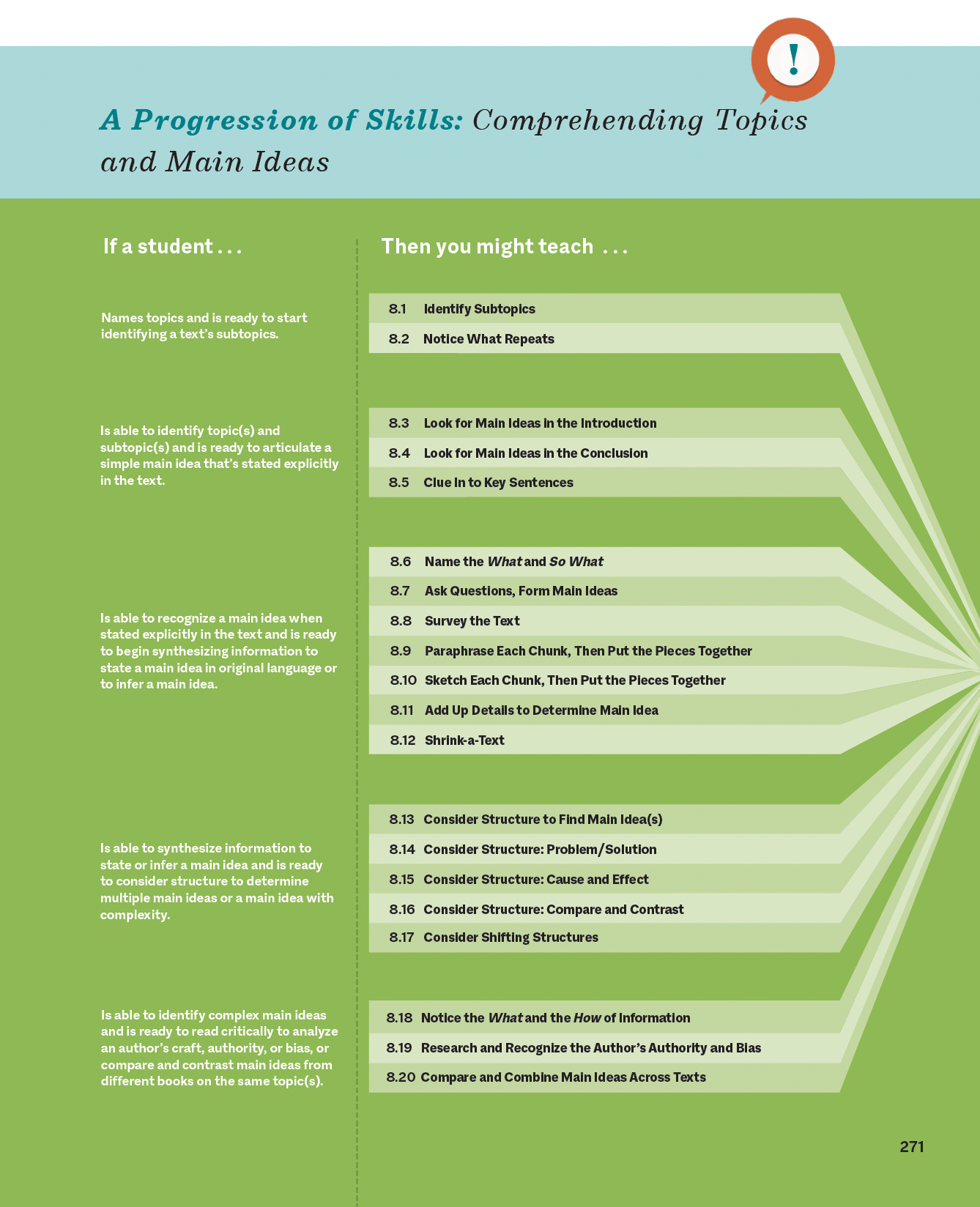
For instance, a student working to comprehend main ideas in increasingly complex texts might progress from identifying clearly stated main ideas to inferring multiple main ideas across different sections, and eventually to synthesizing dense text content with various text features to determine complex, nuanced main ideas.
For readers at the beginning of this skill progression, a strategy to identify subtopics helps them organize information into meaningful chunks as they read and then determine to how these related ideas connect and build toward a book's overall main idea.
For readers at the end of this skill progression, a strategy about how to investigate an author's background helps students identify potential bias and perspective, which clarifies the angle from which main ideas are presented and how they interconnect.
[Download your own copy of 13 skill progressions, organized by goal, in English or Spanish]
Leveraging Skill Progressions: Writing Instruction
Start with student writing: examine samples to identify a specific writing goal the student needs to work toward. Next, refer to the skill progression associated with that goal and consider where the student currently falls along the continuum of development. Ask yourself, 'What feels like a logical next step to teach this writer based on what they are currently doing?' This approach ensures you select strategies that not only respond to individual student needs but also align with the specific writing format students are working in and the standards-based skills they need to master.
For instance, a student working on elaboration in narrative writing might progress from adding
simple descriptive details about characters and actions to incorporating varied elaboration techniques like dialogue, internal thinking, and sensory details. Eventually, they advance to layering these techniques purposefully—using figurative language, precise word choice, and strategic pacing to build tension, develop themes, or reveal character complexity.
For writers at the beginning of the skill progression, a strategy that encourage them to act out a story allows them to generate more specific details to include in their narratives. Instead of simply writing "I was walking to school," a student who acts out the scene can more readily mention stopping to retie a shoe, a sudden loud noise, etc.
For writers near the end of the skill progression, a strategy about using imagery to make facts come alive helps older writers transform research into vivid, engaging elaboration by connecting facts to sensory and descriptive language. Instead of simply writing that penguins entered the water, they might craft evocative language, provide comparisons, include sensory imagery, etc.
[Download your own copy of Writing Skill Progressions, organized by genre and goal.]
Using Skill Progressions to Support Student Self-Reflection
Reframe skill progressions into student-friendly, age-appropriate language, which makes it easier for students to understand. Translate technical phrasing into clear statements that help learners recognize what progress looks like in their own reading and writing and what their next steps might be. Then invite students to reflect on their work by asking questions such as, “Which statement best describes your reading or writing right now?” or “What is your next goal?” These brief, consistent moments of reflection help students name their strengths, set realistic goals, build metacognitive awareness, and take greater ownership of their learning.
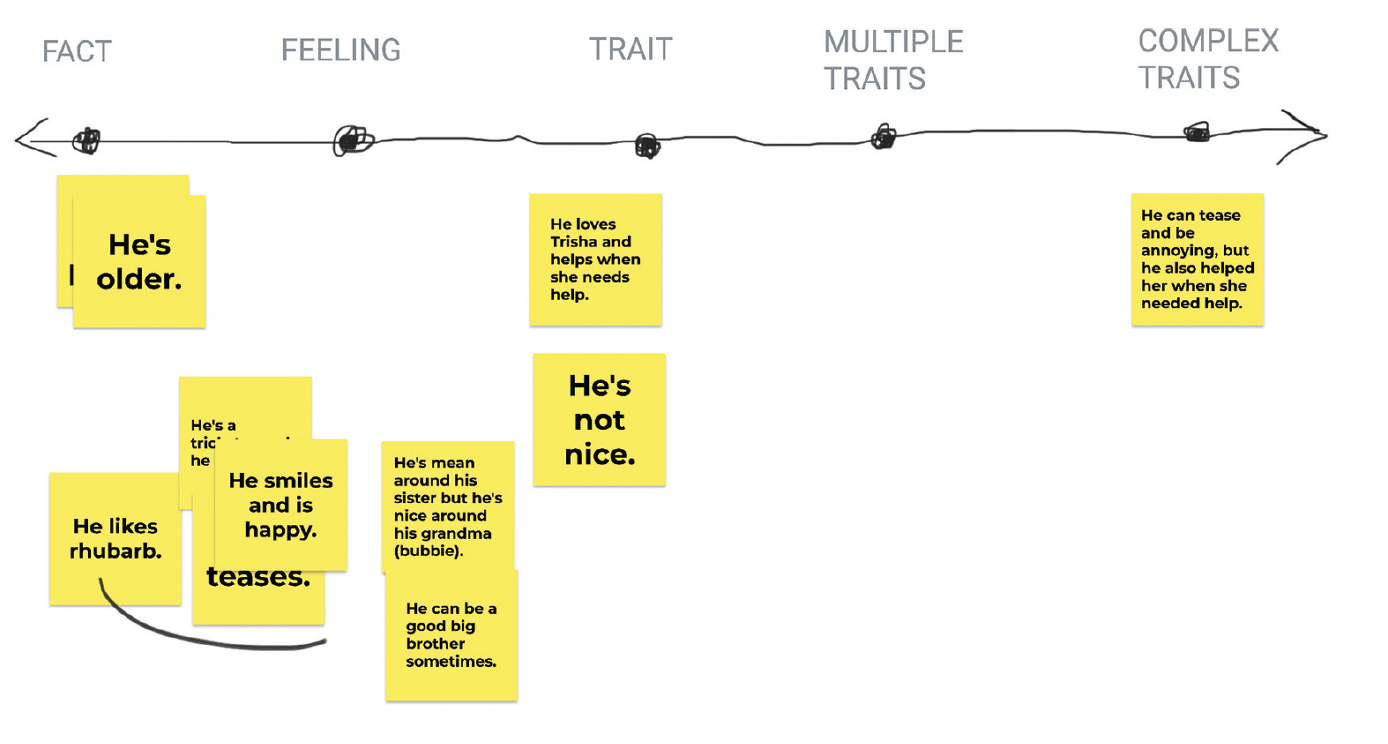
For example, during a read aloud, engage students in self-reflection about character development might look like. Invite students to stop and jot their ideas and thinking about a character on sticky notes. Then place the sticky notes under a document camera and guide students in working together to sort them into categories that reveal different facets of the character.
Younger students might group notes that identify basic facts such as the character’s age, size, or appearance. As students further develop their skills, they will shift from simply noticing details to infer a character’s feelings, and then traits. With continued growth, students can notice complexity, naming multiple or even conflicting feelings at the same time.
When we use skill progressions strategically—matching them to assessment data, selecting targeted strategies, and inviting students into the process through self-reflection—we transform these frameworks from static roadmaps into dynamic instructional tools. By meeting students exactly where they are and guiding them toward their next steps with precision and purpose, we ensure that every learner receives the right support at the right time to advance their literacy skills.
***
Download your own copies of skill progressions for reading and writing, check out the new edition of The Reading Strategies Book 2.0 where all 300+ strategies are aligned to goal-based skill progressions, and learn more about how to use skill progressions to guide reflection in reading and writing goal-setting in Teaching Reading Across the Day and Teaching Writing in Small Groups.